French Bulldogs, affectionately known as “Frenchies,” have captured the hearts of dog lovers worldwide. Their compact size, bat-like ears, and affectionate temperament make them a popular choice for families, singles, and even those in need of emotional support animals. In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about French Bulldogs, from their history and characteristics to their health, grooming, and training needs. Additionally, we will delve into how they can be trained as emotional support or service animals.
Key Characteristics of French Bulldogs
French Bulldogs are a small breed, generally weighing between 16-28 pounds. They have a muscular build, compact body, and distinct bat-shaped ears that stand erect. Their short coat comes in a variety of colors, including:
- Brindle
- Fawn
- White
- Black.
Despite their small stature, Frenchies possess a confident, playful personality.
They are known for being loyal companions with a tendency to form strong bonds with their owners. French Bulldogs are generally good with children and other pets, making them a suitable choice for families. However, their stubborn nature can sometimes pose challenges during training, requiring patience and persistence.
History of the French Bulldog
The French Bulldog’s origin can be traced back to 19th-century England, where they were initially bred as smaller versions of the English Bulldog. Lace workers from Nottingham who moved to France during the Industrial Revolution brought their small Bulldogs with them. These dogs gained popularity in France, where they were bred with local ratting dogs, giving rise to the French Bulldog we know today. By the late 1800s, the breed had become fashionable among the French upper class and eventually gained international recognition. Today, French Bulldogs are among the most popular breeds in many countries, including the United States.

Common Health Issues
Brachycephalic Syndrome
French Bulldogs have a flat face, which classifies them as a brachycephalic breed. This anatomical feature can lead to breathing difficulties, particularly in hot or humid weather. Owners should avoid over-exercising their Frenchies and be cautious during extreme temperatures to prevent respiratory distress.
Hip Dysplasia
Though more common in larger breeds, French Bulldogs can suffer from hip dysplasia, a condition where the hip joint doesn’t develop correctly. This can cause pain, stiffness, and difficulty in movement. Keeping your dog at a healthy weight and providing joint supplements may help manage this issue.
Allergies
French Bulldogs are prone to allergies, which can manifest as skin irritations, ear infections, or digestive issues. Common allergens include certain foods, environmental factors, and parasites. Regular grooming and a proper diet can help reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Grooming Needs
French Bulldogs are relatively low-maintenance when it comes to grooming, thanks to their short coat. However, regular care is still necessary to keep them healthy and looking their best.
Brushing
French Bulldogs shed moderately, so brushing their coat once or twice a week can help remove loose hair and reduce shedding. A soft-bristle brush or grooming mitt is ideal for this task.
10 Best Brushes for French Bulldogs
Bathing
Frenchies do not require frequent baths, but they should be bathed every 4-6 weeks or when they become particularly dirty. Be sure to use a dog-specific shampoo to avoid skin irritation.
Facial Folds
One area that requires special attention is the facial folds. These folds can trap moisture, dirt, and bacteria, leading to infections if not cleaned regularly. Use a damp cloth or specialized wipes to clean the folds every few days.
Nail Care
Like all dogs, French Bulldogs need regular nail trimming to prevent overgrowth, which can cause discomfort or affect their walking.
Exercise and Training Requirements
Despite their small size, French Bulldogs are energetic and require regular exercise to stay healthy and mentally stimulated. However, due to their brachycephalic nature, they are not built for intense physical activity, and owners should avoid over-exertion.
Exercise
A moderate daily walk, along with some playtime indoors, is usually sufficient to meet their exercise needs. Be cautious during hot weather, as French Bulldogs are prone to overheating.
Training
Training a French Bulldog can be both rewarding and challenging. Their intelligence makes them quick learners, but their stubborn streak can lead to resistance. Consistency, patience, and positive reinforcement methods work best with this breed.
In addition to basic obedience training, it’s important to address any behavioral issues early on. Socializing your Frenchie with other dogs and people from a young age will help prevent shyness or aggression later in life.
Nutrition
A balanced diet is key to keeping your French Bulldog healthy and energetic. Here are some general tips for their nutrition:
High-Quality Dog Food
Choose a high-quality dog food that meets the breed’s nutritional needs. The diet should be rich in protein, moderate in fat, and contain essential vitamins and minerals to support their overall health.
Recommended Dog Food for Frenchies 2024
Portion Control
French Bulldogs are prone to obesity, so it’s important to monitor their portion sizes and avoid overfeeding. Dividing their meals into two smaller portions per day can help prevent overeating.
Allergies and Sensitivities
Since French Bulldogs are susceptible to allergies, you may need to experiment with different foods to find what works best for your dog. Some may benefit from grain-free or limited-ingredient diets if they have food sensitivities.

Emotional Support Animal (ESA) and Service Dog Roles
French Bulldogs, with their friendly and affectionate nature, can make excellent emotional support animals (ESA) and, in some cases, service dogs. Here’s what you need to know about both roles.
Emotional Support Animal
An ESA provides comfort and emotional support to individuals suffering from mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, or PTSD. French Bulldogs’ strong bond with their owners and their calming presence makes them ideal candidates for this role. To qualify for an ESA, you’ll need a letter from a licensed mental health professional stating the need for emotional support.
There are no specific training requirements for ESAs, but basic obedience and good behavior in public are essential.
Service Dog
While French Bulldogs can serve as ESAs, they are less commonly used as service dogs due to their size and physical limitations. However, they can still perform specific tasks for individuals with disabilities, such as alerting to anxiety attacks or retrieving small objects.
Training a service dog is more intensive; however, may be completed by a handler under federal law. Additionally, service dogs have legal protection under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), allowing them to accompany their owners in public places where pets are typically not allowed.
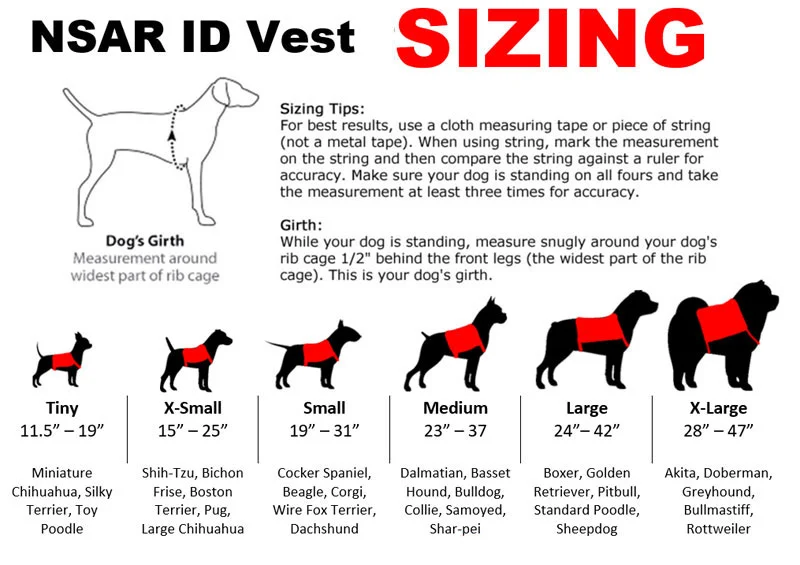
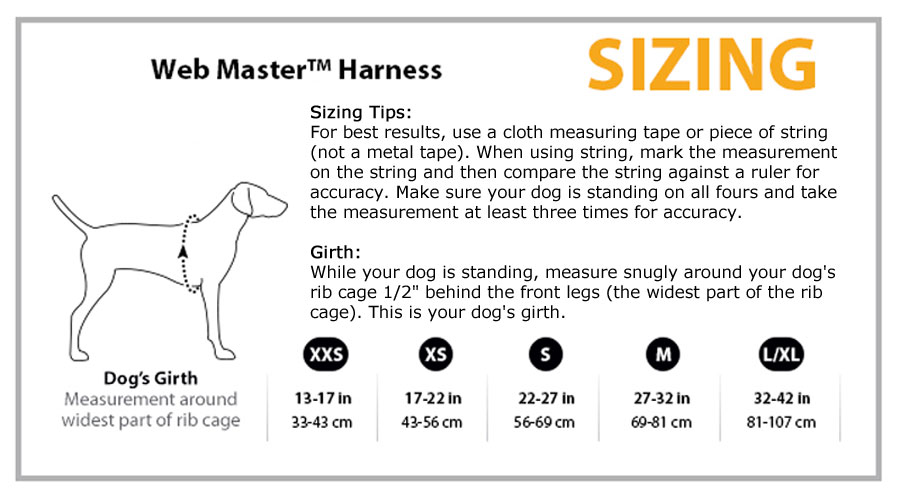
Legitimize the look of your service dog with NSAR’s Service Dog Identification Kits
Legal Aspects of ESAs and Service Dogs
It’s important to understand the legal differences between emotional support animals and service dogs:
Emotional Support Animals are not granted the same public access rights as service dogs but are allowed to live in housing that otherwise prohibits pets, thanks to the Fair Housing Act. This doesn’t mean you cannot take them out in public; however, it’s management’s discretion to grant access, so we recommend you call ahead to obtain approval so that you’re not met with any resistance upon entering their establishment.
Service Dogs, on the other hand, have full public access rights, including entry to restaurants, stores, and public transportation. These dogs must be specifically trained to perform tasks related to their owner’s disability.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial when deciding whether to pursue an ESA or service dog status for your French Bulldog.
Conclusion
French Bulldogs are loving, loyal companions with many unique traits and needs. From their charming history to their common health concerns, grooming, and training requirements, owning a Frenchie requires dedication and attention to their well-being. Whether you’re considering a French Bulldog as a family pet, an emotional support animal, or even a service dog, this breed’s versatility and affectionate nature make them an excellent choice for many different lifestyles.