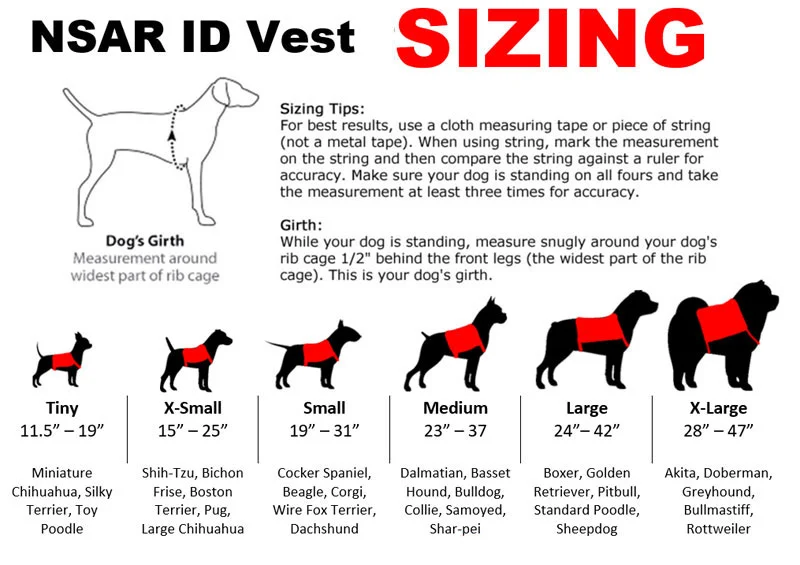
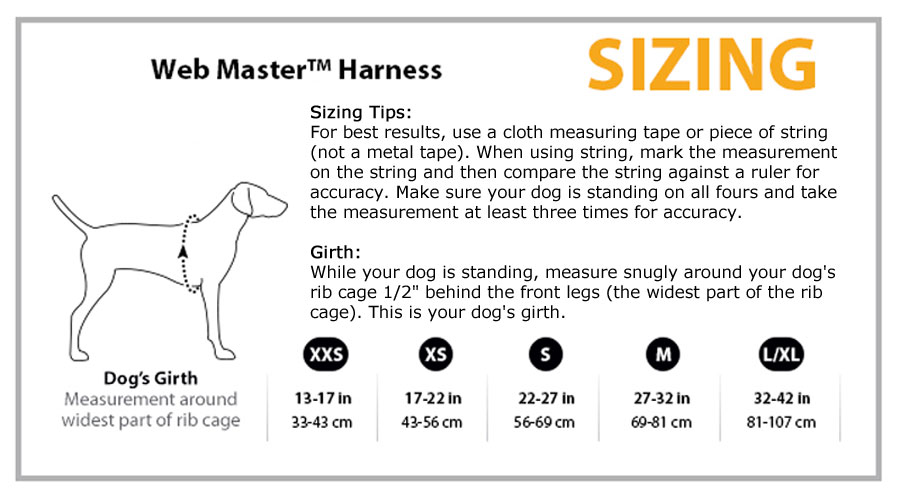
Service animals are becoming a more common sight in society. Many people benefit from service animals for both practical and therapeutic reasons. For those who suffer from a range of debilitating conditions, service animals can help restore quality of life and provide peace of mind to those who use them. The Americans with Disabilities Act protects the rights of those who use service animals, and as a result of federal regulations, service animals are more accepted now than ever before.
However, that doesn’t mean there aren’t still myths, misconceptions, and inaccuracies present when it comes to service animals, the regulations that govern their usage, and the people who benefit from their service. Whether you have a service dog who performs specific tasks for you or an Emotional Support Dog (ESA dog) whose presence helps to mitigate the effects of psychological or emotional issues, you may encounter some of the following myths as you navigate the world with a service animal. Read on to learn more about some of the most common misconceptions pertaining to emotional support animal myths and discover the best ways to debunk them.
Myth 1: All Service Animals Are the Same
While it may be convenient to lump all service animals into one category, they actually fall into three distinct categories that are determined by the type of service they provide to their owners. Service dogs are canines that receive special training to perform tasks that their owners may not be able to complete themselves due to a specific disability.
Emotional support animals (ESA) aren’t trained to perform tasks but are instrumental in helping those who suffer from emotional and psychological conditions function in society. While not considered service dogs, ESAs can be legitimized with a letter from a licensed health care provider and ESA registration. Therapy dogs represent yet another class of service animal. They are similar to ESAs in the function they fulfill. However, instead of being assigned to a single owner, they are often used in group settings so that their benefits can be enjoyed by many people rather than a single owner.
Myth 2: Anyone Can Get an ESA
While it may be true that anyone can have a pet that brings emotional support and psychological benefits, that doesn’t necessarily mean that your dog or other animal qualifies as an ESA. For a pet to truly be formally considered as an ESA, a licensed mental health professional, such as a psychotherapist, psychiatrist, or licensed mental health social worker must determine that an ESA will benefit you. Once the determination is made, the care provider issues a letter to legitimize your ESA. Those letters must be renewed each year to remain valid.
Myth 3: Only Service Dog Owners are Protected from Discrimination
Numerous pieces of legislation protect the rights of those who must use ESAs from being barred from public transportation, housing opportunities, and public facilities. For example, the Fair Housing Act protects the rights of tenants to keep their ESAs even when the landlord has an explicit ‘No Pets’ policy. Not only that, there is no charge for keeping the ESA. Landlords may however request to see documentation like an ESA letter for housing that proves the tenant’s need for an ESA. This protects the landlord from being duped and tenants from being discriminated against.
Housing is likewise protected for those with ESAs by the Fair Housing Act, as landlords can’t discriminate against those with emotional support dogs and can’t charge additional fees for the animals. The Americans with Disabilities Act prohibits employers from discriminating on the basis of disability and are required to make reasonable accommodations for the disabled. Those clauses extend to those who use ESAs, and employers can’t use emotional support animals as a reason to discriminate against job candidates or employees. However, hotels and restaurants aren’t required to grant access to those with emotional support dogs, though they are required to do so with service dogs.
Myth 4: ESA Dog Rules Vary by State
Service dog and ESA rules aren’t set at the state level but are instead governed by federal law. While there may be state regulations in place that augment or enhance access for those who use service animals and ESAs, the core rights of those who use both categories of animals are protected at the federal level by legislation such as the Americans with Disabilities Act, the Fair Housing Act, and the Air Carriers Access Act.
If you think you could benefit from the use of a service animal or ESA, consider these myths when making an informed decision. To learn more about misconceptions surrounding service animals, visit the National Service Animal Registry.
Myth 5: Only Dogs Can be ESAs
Various domesticated animals, in addition to dogs, can qualify as emotional support animals. For example, ESAs can be cats, rabbits, ferrets, pigs, birds, and even miniature horses. An ESA should be well-mannered and not cause a nuisance to others. If your emotional support animal is a dog, it can be of any breed and size. However, this isn’t applicable to service animals since the ADA recognizes only dogs as service animals. It is important to note that an ESA is not considered a pet since it is essentially doing a job of providing you relief from your emotional disability through companionship.
Myth 6: All Emotional Support Animals are Service Animals
This is one of the common Emotional Support Animal myths. Emotional Support Animals are not service dogs. A service dog is specifically trained to perform certain tasks related to the disability of its handler. For example, a service dog can fetch medication and water, respond to seizures, pull a wheelchair, create a barrier between its handler and other people, interrupt self-harm, get help, act as a guide dog for the visually impaired, alert its handler, switch on lights, etc. But an ESA does not receive any formal training of this sort. The job of an ESA is to provide comfort and companionship to a person who is suffering from an emotional or psychiatric disability.
Myth 7: Anyone Can Get an ESA or a Service Animal
Typically, anyone who owns a pet draws emotional support and companionship from them. However, this does not make the pet an emotional support animal or service dog. To get an ESA or a service dog, you need intervention from a licensed mental health practitioner (LMHP). An LMHP will first evaluate your mental health to determine whether you need one. Not everyone with a disability will need an ESA or a service dog. The responsibility of caring for an animal may become overbearing for some people. If your LMHP feels that your treatment can be augmented with an ESA and if you already own a pet, they will also verify whether the animal can provide emotional support and psychological benefits in times of need. If everything checks out, you will be issued a legitimate ESA letter.
Myth 8: Airline Carriers Have to Allow You to Fly with Your ESA in the Cabin
Previously, both ESAs and service dogs were covered under the Air Carrier Access Act which meant handlers could fly with them in the cabin without charge. Many people started taking advantage of the system and brought along poorly trained animals with them which caused a lot of inconvenience for fellow passengers. So in 2021, the rules were changed to exclude ESAs who now have to travel in a carrier with or without an ESA letter. Only service dogs who are trained to perform tasks related to physical, psychiatric, sensory, intellectual, or mental disabilities can travel in the cabin. Since this rule has come into effect recently, there has been a lot of speculation over it, which is why it has become a common emotional support animal myth.
Myth 9: You Can Take Your ESA or Service Animal Anywhere
Although you can stay with your ESA or service animal in an accommodation that does not allow pets, the same may not be applicable to all public places or business facilities. For example, non-pet-friendly grocery stores, restaurants, etc. may not allow your ESA. However, this is not always the case with service animals. A service animal can accompany you to movie theatres, restaurants, schools, museums, etc. Covered entities are required to modify their policies to accommodate a service animal. That being said, businesses hold the right to exclude the animals from their premises if their presence jeopardizes the safety of others. For example, if a service animal is not housebroken or is out of control, businesses may ask the handler to remove it from the facility. Hospitals may not allow such animals in the operating room, etc.
Myth 10: You Cannot Get a Legitimate ESA Letter Online
While being a common emotional support animal myth, it cannot be any further from the truth. The basis of this myth is the rising number of fraudulent companies that scam people with fake ESA letters. This is why it is important to be cautious. One of the ways to identify the legitimacy of an ESA letter is through the intervention of an LMHP.
National Service Animal Registry provides a platform to order legitimate ESA letters. Once the order is placed, you will need to answer a set of questions. Based on your answers and your zip code, an LMHP will be assigned to you who will diagnose your condition and determine whether an ESA is necessary. If approved, an ESA letter will be provided to you on the official letterhead of the LMHP. Get your ESA letter today.
If you think you could benefit from the use of a service animal or ESA, consider these myths when making an informed decision. To learn more about misconceptions surrounding service animals, visit the National Service Animal Registry.